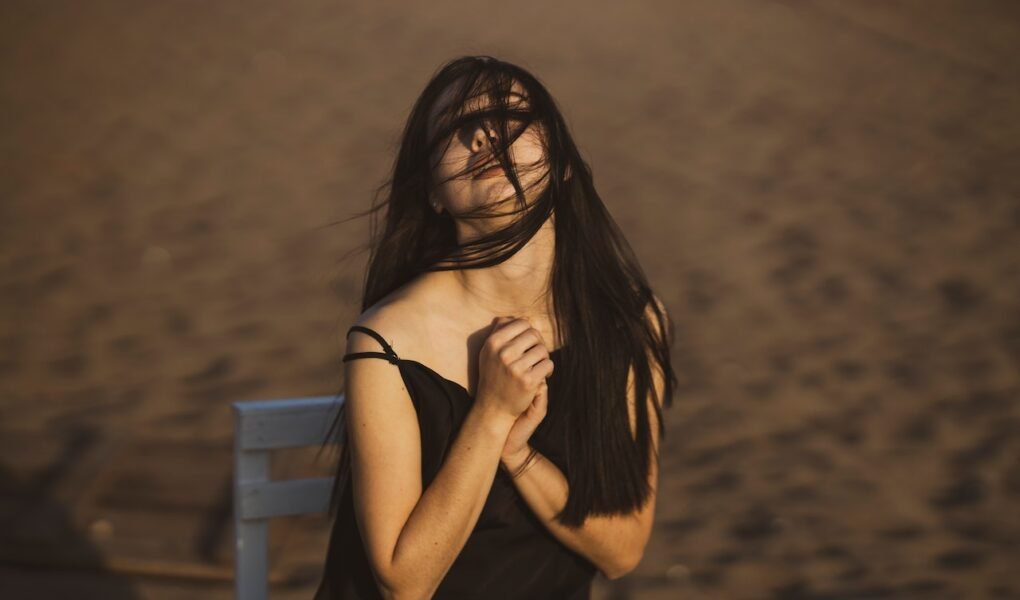
Emotions are an integral part of the human experience, shaping our thoughts, actions, and interactions. While we often think of emotions as singular entities, the world of psychology distinguishes between two fundamental categories: primary emotions and secondary emotions. In this exploration, we dive deep into the realm of emotions to understand the key differences between primary and secondary emotions and their significance in our lives.
Understanding Primary Emotions
Definition and Characteristics of Primary Emotions
Primary emotions, often referred to as basic emotions, are innate, instinctive, and universally experienced by humans across cultures and ages. These emotions are hardwired into our biology and serve as immediate responses to specific stimuli.
Examples of Primary Emotions
- Joy: The unmistakable feeling of happiness and delight, often accompanied by a smile and positive body language.
- Anger: A powerful and often intense emotion associated with displeasure, frustration, or the perception of a threat.
- Fear: The instinctual response to danger or perceived threats, triggering a “fight or flight” reaction.
- Sadness: The emotional response to loss, disappointment, or feelings of powerlessness.
- Disgust: The repulsion or aversion felt toward something unpleasant or offensive.
- Surprise: The sudden, unexpected reaction to something novel or unforeseen.
The Evolutionary Significance
Primary emotions have evolved as adaptive responses to ensure human survival. For example, fear helped our ancestors respond quickly to threats, while joy reinforced positive behaviors and social bonds. These emotions served as essential tools for navigating a hazardous world.
Exploring Secondary Emotions
Definition and Relationship with Primary Emotions
Secondary emotions, in contrast to primary emotions, are complex and often arise from the interplay of multiple primary emotions. These emotions are not as universally experienced and can vary across individuals and cultures.
The Concept of Blending Emotions
- Secondary emotions frequently result from the blending or mixing of primary emotions. For instance, jealousy may stem from a combination of fear, anger, and sadness.
- Secondary emotions tend to be more nuanced and require cognitive processing.
The Influence of Social and Cultural Factors
Secondary emotions are significantly influenced by social norms, cultural values, and personal experiences. How emotions are expressed and understood can vary widely across cultures and societies.
Primary Emotions vs. Secondary Emotions: A Comparative Analysis
Nature and Origin
- Primary emotions are instinctual and innate, originating from deep within our evolutionary history.
- Secondary emotions are more learned and shaped by individual experiences and cultural contexts.
Universality vs. Variability
Primary emotions are considered universal, transcending cultural boundaries and language barriers.
Secondary emotions exhibit significant variability, with their interpretation and expression subject to cultural and situational differences.
Function and Expression
- Primary emotions serve as immediate responses to external stimuli, helping us react quickly to threats or opportunities.
- Secondary emotions often involve complex cognitive processes and can be influenced by past experiences, memories, and social conditioning.
Practical Implications
- Emotional Self-Awareness: Understanding the distinction between primary and secondary emotions can enhance emotional self-awareness. Recognizing the primary emotions that contribute to complex emotional states empowers individuals to address their feelings more effectively.
- Communication and Interpersonal Relationships: Knowledge of primary and secondary emotions can improve communication skills by allowing individuals to express themselves more clearly. An empathetic understanding of others’ emotional complexities is essential for fostering healthy relationships.
Coping with Complex Emotions
Strategies for Managing Secondary Emotions
Techniques for identifying and addressing the primary emotions that contribute to secondary emotions. Coping mechanisms for dealing with complex emotional states effectively.
Seeking Professional Help
Recognizing when to seek therapy or counseling for managing intense or persistent secondary emotions.
The role of mental health professionals in helping individuals navigate complex emotional challenges.
The Ongoing Exploration of Emotions
Acknowledging that the study of emotions is an evolving field with ongoing research and discoveries.
Encouragement for readers to delve further into the fascinating world of emotions and their profound impact on human behavior.
This comprehensive article offers a deep dive into the world of emotions, distinguishing between primary and secondary emotions and elucidating their roles in our lives. Understanding these distinctions can empower individuals to navigate their emotional landscapes with greater clarity and effectiveness.